
 Product Design
Product Design

 Rapid Prototyping
Rapid Prototyping
 CNC Prototyping
CNC Prototyping Rapid Prototyping
Rapid Prototyping Stereolithography Apparatus (SLA)
Stereolithography Apparatus (SLA) Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
 Custom Molds - Plastic Molds
Custom Molds - Plastic Molds

 Plastic Molding
Plastic Molding

 Production Tooling
Production Tooling

Plastic Molding – Blow Molding
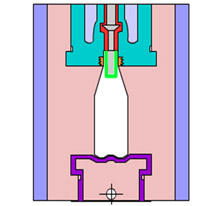 Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow, thin-walled plastic objects such as bottles and containers, cases and bellows.
Blow molding is a manufacturing process used to create hollow, thin-walled plastic objects such as bottles and containers, cases and bellows.
A typical blow molding process begins with a heated hollow thermoplastic tube, also known as preform or parison. The plastic tube has a hole in one end, allowing compressed air to enter. The plastic is inflated into the closed chamber of a divided mold to conform to the shape of the mold’s cavity. The molded plastic is left to cool and harden. Once released from the mold, the plastic part can be processed to have the holes rimmed or residues trimmed.
Some plastics are not suitable for blow molding. The most frequently used materials are:
- Low Density Polyethylene (LDPE), High Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
- Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)
Interested or any question, please contact us.
 We are constantly looking for new products in order to grow our business and Invention Home has enabled us to streamline that process much more quickly.
We are constantly looking for new products in order to grow our business and Invention Home has enabled us to streamline that process much more quickly. Marsha Dunmyre
CA, U.S.A
BROWSE MORE
Cool Prototyping provides "one-stop" product design service: rapid prototyping, plastic molds, custom molds, production tooling and plastic molding.
Cool Prototyping Copyright 2008-2009 © All Rights Reserved. Rapid Prototyping
Cool Prototyping Copyright 2008-2009 © All Rights Reserved. Rapid Prototyping

